Vitamin D3 K2 Drops – Liposomal Vitamin D3 with High Bioavailability
Our LipoVibes Vitamin D3 K2 drops combine the “sunshine vitamin” D3 with vitamin K2 – in a highly bioavailable, liposomal form. This combination supports the body in absorbing and effectively utilizing calcium, helps maintain normal bones and teeth, and contributes to normal muscle function as well as a healthy immune defense.
Thanks to the patented LipoMolecule™ technology, vitamin D3 is encapsulated in tiny lipid particles that resemble cell membranes. This way, the active ingredient reaches the cells directly, without unnecessary loss, and is made quickly and effectively available to the body.
Especially during the low-sun months or when spending most time indoors, sufficient vitamin D3 supply is often difficult. In combination with vitamin K2, it ensures that absorbed calcium is optimally stored in the bones rather than remaining in the blood vessels.
Why You Should Choose LipoVibes Vitamin D3K2
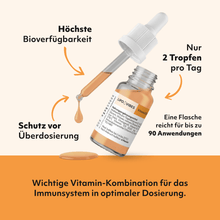
1. Individual absorption in the body: Our scientifically developed nutrient transport system delivers precisely the right amount of essential vitamins and active ingredients to your cells.
2. Patented overdose protection: The unique protection mechanism reliably prevents overdosing – in a purely natural way.
3. Controlled manufacturing: Our LipoVibes products are developed in our laboratories in Germany and produced according to strict quality standards using only plant-based ingredients. They are vegan and free from sugar, gluten, lactose, and GMOs.
What is Vitamin D3?
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is a fat-soluble vitamin that the body can produce itself with sufficient sunlight exposure. It plays a key role in calcium and phosphorus balance and is therefore essential for maintaining normal bones, teeth, and muscle function. It also contributes to normal immune system function and supports numerous cellular processes important for vitality and well-being. Since the body’s own production can decrease significantly during low-sun months or with an indoor lifestyle, targeted supplementation is often useful.
LipoVibes Vitamin D3 and K2 – Perfectly Matched
Vitamin D3 unfolds its full effect only when calcium is properly distributed in the body. This is where vitamin K2 comes into play: it supports the transport of calcium to where it is needed – into bones and teeth – while preventing it from depositing in blood vessels.
The combination of vitamin D3 and K2 in liposomal form ensures optimal synergy. While vitamin D3 regulates calcium levels, vitamin K2 directs the mineral precisely to the right places.
In LipoVibes Vitamin D3 K2 drops, we use only highly pure, plant-based vitamin K2 in its most effective form, MK-7, combined with bioavailable vitamin D3. The result is effective support for bone strength, muscle power, and cardiovascular health – in a form the body can absorb especially well.
LipoVibes Vitamin D3 K2: Premium Sourcing
Our vitamin D3 is carefully extracted from lichen, a natural organism that produces vitamin D3 under UV light. Gentle extraction preserves the valuable substance in its natural form, allowing your body to absorb it optimally. We focus on the highest purity and sustainability: our lichen comes from controlled sources, free from animal components and artificial additives. This way, LipoVibes combines plant-based purity with premium quality for your daily health.
Vitamin D3 Benefits: Essential for Body Functions and Well-being
Vitamin D3 fulfills many roles in the body. It supports calcium absorption, regulates important metabolic processes, and contributes to muscle and nervous system function. In this way, vitamin D3 supports a balanced and active lifestyle.
Key areas of vitamin D3 action at a glance:
- Bone health: Supports calcium absorption in the intestine and its storage in the bones.
- Calcium metabolism: Contributes to regulating calcium levels in the blood and supports normal muscle function.
- Immune system: Supports the normal function of the immune system.
- Inflammatory processes: Contributes to the body’s normal response to inflammation.
- Cardiovascular system: Supports the normal function of blood vessels and cardiovascular processes.
- Neurological functions: Contributes to the normal function of nerve cells.
- Muscle health: Supports muscle function and strength.